Post written by Shinji Tanaka, MD, PhD, from Endoscopy and Medicine, Graduate School of Biomedical & Health Sciences, Hiroshima University, Japan.
By JNET classification using magnifying observation, it will be possible to characterize the lesions of NICE Type 2 more in detail. NICE Type 2 includes various lesion such as dysplasia, superficial submucosal carcinoma, and deep submucosal carcinoma. It has been required to distinguish between dysplasia and submucosal carcinoma.
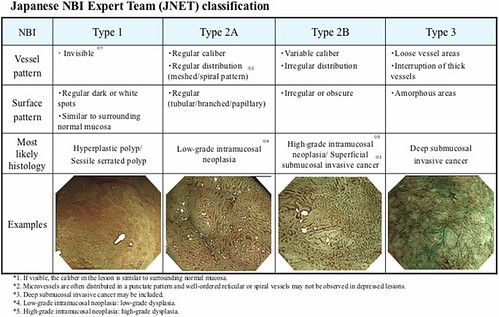
Figure 1. Japanese NBI Expert Team classification system.
NICE Type 1 is an indicator for hyperplasia/SSP, and Type 3 is an indicator for deep submucosal carcinoma. JNET classification Type 2A and 2B are nearly equal to the subclassification of NICE Type 2. As a result, JNET classification Type 1 stands for hyperplastic polyp (HP) and sessile serrated polyp (SSP). Type 2A stands for low-grade dysplasia (LGD), such as tubular adenoma/tubulovillous adenoma. Type 2B stands for high-grade dysplasia (HGD) and superficial submucosal invasive carcinoma (SM-s carcinoma), and Type 3 stands for deep submucosal invasive carcinoma (SM-d carcinoma). Although the diagnostic performance of JNET Type 2B is a little low, it enables characterization of the NICE Type 2 lesions and contributes to the selection of therapeutic procedures, such as piecemeal EMR, ESD, or surgery.
Find the article abstract here.
The information presented in Endoscopedia reflects the opinions of the authors and does not represent the position of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE). ASGE expressly disclaims any warranties or guarantees, expressed or implied, and is not liable for damages of any kind in connection with the material, information, or procedures set forth.
