Post written by Mimi C. Tan, MD, MPH, from the Section of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas.

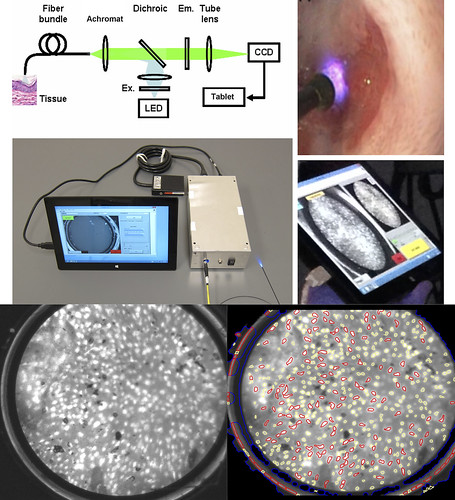
High-resolution microendoscopy (HRME) is an ‘optical biopsy’ technology that provides sub-cellular imaging of esophageal mucosa at the time of endoscopy. The endoscopist is able to assess nuclear size, crowding, and pleomorphisms in real time to determine if an imaged site appears neoplastic or normal. However, most gastroenterologists are not trained to interpret these histopathology-like images. Therefore, we developed a fully automated ‘artificial intelligence’ software algorithm capable of interpreting these HRME images. The inbuilt automated software algorithm uses abnormal nuclear density to classify each HRME image as neoplastic or non-neoplastic. The goal of our study was to compare the diagnostic performance of the software algorithm to endoscopists in diagnosing esophageal squamous cell neoplasia (ESCN).
We found that 13 endoscopists had a mean sensitivity of 84.3%, specificity of 75.0%, and accuracy of 81.1% for ESCN detection. The software had lower sensitivity (76.3%), higher specificity (85.3%), but no significant difference in accuracy (79.4%) compared to the endoscopists. When the endoscopists were given the algorithm read and asked for a computer-assisted diagnosis, the endoscopists maintained their high sensitivity and overall accuracy and significantly increased their specificity to 80.1%. We found that our software algorithm, based on nuclear density and designed for microendoscopic evaluation of ESCN, was non-inferior in overall accuracy to endoscopists, improved the specificity of endoscopists, and increased the endoscopists’ confidence in their diagnosis.
This technology would be best utilized in assisting endoscopists when interpreting difficult HRME images and in low-resource countries without expert microendoscopists. Computer-assisted diagnosis can also provide real-time feedback and training in HRME for novices learning HRME interpretation.
Read the full article online.
The information presented in Endoscopedia reflects the opinions of the authors and does not represent the position of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE). ASGE expressly disclaims any warranties or guarantees, expressed or implied, and is not liable for damages of any kind in connection with the material, information, or procedures set forth.
