Post written by Partha Pal, MD, DNB, MRCP (UK), FASGE, from the Department of Medical Gastroenterology, Asian Institute of Gastroenterology, Hyderabad, India.

Fibrostenotic strictures in Crohn’s disease are particularly challenging when associated with distorted anatomy and pseudopolyps. We describe an endoscopic reconstructive surgery approach using multimodality interventional endoscopy, integrating preprocedural intestinal ultrasound (IUS) with water pressure–assisted endoscopic stricturotomy and targeted mucosectomy/polypectomy to safely restore luminal patency after failure of balloon dilation. This case highlights the role of image-guided, bowel-sparing interventional inflammatory bowel disease techniques for complex strictures.
Conventional endoscopic approaches for Crohn’s disease–related strictures, particularly endoscopic balloon dilation, are associated with high recurrence rates and typically performed without real-time imaging guidance, limiting procedural precision. Complex strictures often require multiple complementary endoscopic techniques, but guidance on how to integrate them safely in a structured manner is limited. We felt it was important to demonstrate an imaging-guided, multimodality endoscopic strategy that allows tailored, stepwise intervention while potentially reducing repeat procedures and preserving bowel integrity.
This article presents that water pressure–assisted endoscopic stricturotomy, combined with targeted mucosectomy and polypectomy, can safely restore luminal patency in a complex Crohn’s disease–related colonic stricture. Preprocedural IUS enabled accurate characterization of stricture length, fibrosis, and upstream dilation, allowing tailored intervention while follow-up IUS provided a noninvasive means to assess response to endotherapy.
To our knowledge, this represents a novel application of water pressure techniques in endoscopic stricturotomy for Crohn’s disease. Future studies should evaluate the reproducibility of this image-guided, multimodality approach and its impact on recurrence rates and need for repeat interventions compared with conventional balloon dilation.
This case underscores the evolving role of interventional inflammatory bowel disease, where imaging-guided endoscopy enables tailored, bowel-preserving solutions for complex disease phenotypes.
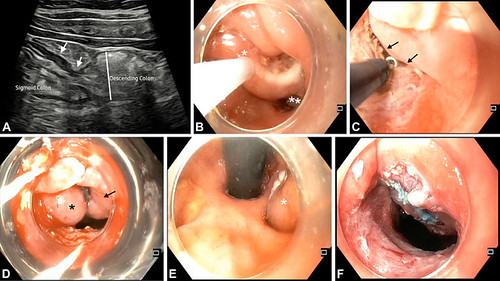
A, Transabdominal ultrasound showing a short-segment fibrotic stricture (arrows) at the sigmoid-descending junction with prestenotic dilation (asterisk). B, Pseudopolyps distal (single asterisk) and proximal (2 asterisks) to the stricture. Piecemeal snare polypectomy being performed for the proximal pseudopolyps. C, Water pressure–assisted endoscopic stricturotomy being performed using an insulated-tip knife; water jet displaces opposing mucosa (arrows) to avoid thermal injury. D, Band ligation performed for protruding folds proximal to the stricture showing inadequate capture: asterisk showing captured fold and arrow showing part of the obscuring fold that is not captured by the band in between. This led to paradoxical worsening as it blocked the stricture opening. E, Retroflexed view from the descending colon poststricturotomy showing obstructing mucosal folds (asterisk) requiring mucosectomy. F, Poststricturotomy, polypectomy, and mucosectomy image with adequate luminal opening.
Visit iGIE’s Facebook, X/Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, and YouTube accounts for more content from the ASGE peer-reviewed journal that launched in December 2022 and has been PubMed indexed.
Read the full article online.
The information presented in Endoscopedia reflects the opinions of the authors and does not represent the position of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE). ASGE expressly disclaims any warranties or guarantees, expressed or implied, and is not liable for damages of any kind in connection with the material, information, or procedures set forth.
